The exact causes of GI lymphoma in cats are unknown although genetics are generally assumed to be the most important factor. 8 A serious known complication of UC is toxic megacolon which is nonobstructive dilation of the colon 6 cm and is.

Inflammatory Bowel Disease In Cats
This slower movement results in abnormal hair collection in the stomach or intestines resulting in hair-ball formation.

. There can be acute episodes caused by many things including viral or bacterial. Another kind of tumor called a diffuse growth can cause a generalized thickening of the overall intestine. Irritable bowel should in general be viewed as a condition that needs to be maintained and controlled rather than cured.
We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website. However edema congestive heart failure cirrhosis of the liver infections parasitic infestations and inflammation can also cause intestinal thickening. Colitis and Proctitis in Cats.
IBD occurs because of chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and can be caused by a number of diseases including bacterial and parasitic infections and food allergies. When inflammation continues over a long period of time normal tissue is sometimes placed by a very fibrous scar tissue. Feline inflammatory bowel disease IBD is a condition in which a cats gastrointestinal GI tract becomes chronically irritated and inflamed.
A muscularis to submucosa ratio 1 is indicative of an abnormal bowel segment. Stomach wall thickening is referred to as gastritis which is divided into two. Out first knowing if a cat has disease of the stomach or small intestine.
Histiocytic ulcerative colitis is a bowel disease which causes the lining of an animals colon to thicken with varying degrees of ulceration and tissue loss to the superficial lining. Thickening of the bowel wall may be focal 40 cm in extension. What Causes Gastrointestinal Lymphoma.
The most common form of intestinal cancer in cats is lymphoma. Certain medical conditions such as a parasitic infection and HIVAIDS also cause the lining of the stomach to thicken as Mayo Clinic explains. Cats with this disease exhibit a chronic infiltration of inflamed cells in the intestine.
The mean thickness of the muscularis propria in cats with lymphoma or IBD was twice the thickness than that of healthy cats and was the major contributor to significant overall bowel wall thickening in the duodenum and jejunum. It can occur as focal tumors which appear and grow in specific locations or as diffuse growth which causes a general thickening of the overall intestinal system. This infiltration invades the walls of the gastrointestinal tract causing them to thicken and disrupting the intestines normal functioning.
The thickening is due to the infiltration of various cells in the layers under the lining. Inflammatory bowel disease IBD Cancer of the intestines. IBD is usually food related but not always.
By contrast inflammatory diseases usually cause long sections of the intestines to. Ultrasonographically there was a segmental intestinal mural mass in all five cats. My kitty has IBD which started when he was only 18 months old.
The mass was characterized by circumferential bowel wall thickening with transmural loss of normal sonographic wall layers. When feline inflammatory bowel causes a diffuse thickening of the bowel wall it may not be distinguishable from feline intestinal cancer. Inflammatory cells infiltrate the walls of the GI tract thickening them and disrupting the ability of the GI tract to properly digest and absorb food.
IBD and lymphoma create a motility disorder. Inflammatory bowel disease. The thickened stomach wall and intestinal loops do not move hair through the digestive tract at its normal speed.
Perienteric fat stranding disproportionally more severe than the degree of wall thickening suggests an inflammatory condition. Inflammatory bowel disease IBD affects about 50 of cats that have significant intestinal thickening. Other than bowel wall thickening chronic cases of ulcerative colitis demonstrate perirectal fat proliferation and a low-attenuating ring within the bowel wall as a result of submucosal fat deposition called the halo sign.
He has constant runny bowels and pain when he defecates which isvery little at - Answered by a verified Cat Veterinarian. In one cat the circumferential symmetric hypoechoic bowel wall thickening was similar to that reported for segmental lymphoma. Early diagnosis of gastric cancer is one of the most important parameters affecting the survival of the disease.
This pattern is also described with feline inflammatory bowel disease. Gastrointestinal lymphoma is the most common form of lymphoma in the cat. In this study we aimed to stress the importance of antrum wall thickness in CT examination.
IBD can and often does flare which means the thickening would also wax and wane. Focal irregular and asymmetrical thickening of the bowel wall suggests a malignancy. Here is additional information that may help owners of cats affected by this gastrointestinal disease make informed decisions on care and treatment.
The study included 111 patients between ages of 18 and 95 who had antral wall thickening in computed tomography and also had. MD Consult explains that when the colon exhibits short sections of thickening the cause is often some type of colon cancer. If it is a long standing issue then it is some form of IBD.
More recently an ultrasonographic pattern associated with feline small cell T-cell gastrointestinal lymphoma has been recognized as a diffuse thickening of the muscularis propria of the small intestine. The only test that can give you a definitive diagnosis is an intestinal biopsy. To gather more information about what was going on in Tigger x.
Diffuse circumferential thickening of the muscularis layer of the small intestine with preservation of wall layering and the absence of mass formation has been reported in cats with eosinophilic and less commonly lymphocytic enteritis and low-grade small-cell lymphoma. Up to 25 cash back My cat has thickened intestinal walls. The challenge is that both of these diseases have the same symptoms can run in the same age of patient and are not easily distinguishable from each other.
The causes of stomach wall thickening include bacterial infection excessive alcohol use and the body attacking its own cells in the stomach. Cats of any age can be affected by IBD but the disease occurs most often in middle-aged and older. To evaluate the similarities.

Lateral Abdominal Radiograph Of A Cat With Intestinal Plication And Download Scientific Diagram
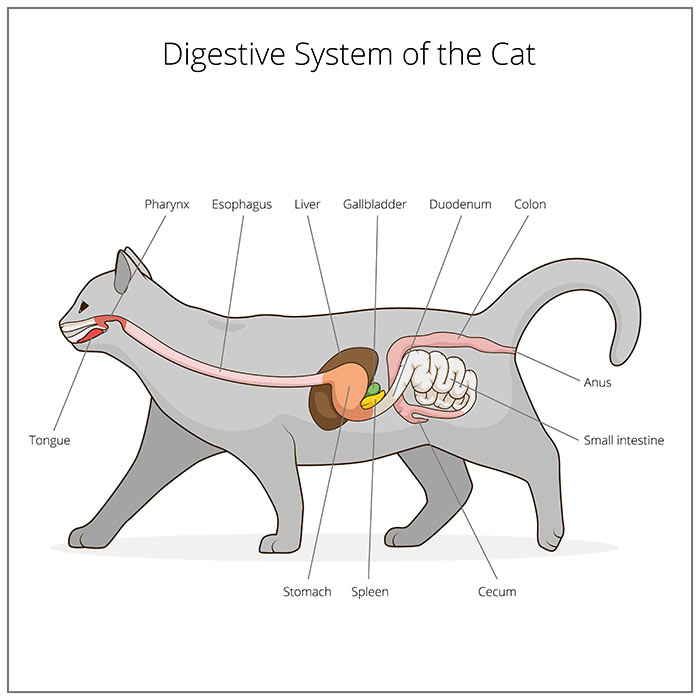
Colitis In Cats What It Is Symptoms Causes Treatment

Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of The Muscularis Propria In Cats With Diffuse Small Intestinal Lymphoma Or Inflammatory Bowel Disease Zwingenberger 2010 Journal Of Veterinary Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library
0 Comments